Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0
Even today, most people associate the “industrial revolution” with steam engines and smoking chimneys. Of course, we also know that production processes have changed significantly since then because progress cannot be slowed down. For a few years now there has been a new specter in the media: “Industry 4.0.” Everyone has heard of it before, and everyone has their own ideas about what’s behind it.
The catchy term “Industry 4.0” was coined at the Hanover Trade Fair in 2011 by a group of German scientists, managers, and politicians to describe and promote general developments in industrial production.
In general, people like to talk about the “fourth industrial revolution” – after mechanization, the assembly line, and the introduction of robots.
The Four Criteria
that characterize industry 4.0
The internet has changed the way people communicate. Now with its decentralized structures, the internet controls the processes on the factory floor as the industrial internet of things (IIoT). Industry 4.0 is characterized by four criteria.

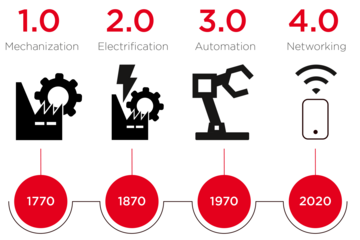
- Networking: In its early days, the Internet was first used to connect people and thus make it easier for them to access information. In industry 4.0, this exchange of information is no longer limited to people. Machines, sensors, and employees are in constant contact with each other and communicate via IIoT.
- Transparent information: Sensors not only provide all the data a machine needs for its work, but they also provide information on numerous other factors such as the condition or availability of a facility. For example, the decision maker has the option of identifying critical points in the production chain or initiating the maintenance of a machine before its productivity decreases.
- Technical assistance systems: The data collected by sensors is processed by assistance systems and made available to decision makers. On this basis, those responsible can make well-founded decisions and react more quickly to possible problems. Other systems support people in strenuous, unpleasant, and dangerous tasks.
- Decentralized structure: In contrast to previous systems, the control system in Industry 4.0 is no longer centralized and strictly hierarchically structured. In daily operations, the individual so-called cyber-physical systems (CPS) work as independently as possible and coordinate with their CPS “colleagues.” Only in exceptional situations is a higher authority informed, which then assumes control.
Planned Revolution
a vision becomes reality
Contrary to the industrial revolutions of the past, this time the innovations will not be set free by a few pioneers. Projects, initiatives, and work groups have been set up worldwide to deal with “Industry 4.0.” Politicians, scientists, and businesses have worked close together from the very beginning.
While the upheavals of the past were mostly driven by the attempt to create a market advantage for one’s own company through technical innovations, this time it is rather a vision for society as a whole that is to be implemented with combined forces. Some goals have already been achieved, but there is still a lot to be done in other areas.
As with all major upheavals, there are two main groups in the current debate: The visionaries who see a golden future and the doubters who warn about catastrophic consequences. Of course, the fourth industrial revolution will also change society, but for the first time there is an opportunity to control these consequences. Critics are already urging politicians to react to the expected change at an early stage.
More efficient and flexible processes. The above-mentioned principles of industry 4.0 are intended to make production processes more efficient and flexible. Experts agree that man will also continue to play a crucial role in the use of “intelligent” machines - as an important control and decision-making authority that quickly oversees complex interrelationships.
This development began in the last industrial revolution with the use of industrial robots and will be intensified by Industry 4.0. As a result, even the remaining low-skilled tasks will sooner or later be eliminated. Further training and adaptation to new technical conditions will be important components of working life in the future. Manual and intellectual activities will become less and less separable.
The increased flexibility in industry 4.0 also offers the possibility of manufacturing more individually. Whereas industrial production has currently primarily meant the mass production of standardized components, the machines will soon be able to adapt to certain variables without having to be laboriously reset by operating personnel beforehand.
Additive Manufacturing to set a new standard. Production techniques such as additive manufacturing set new standards. Here, for example, the same machine can produce gears in a single order and then screw them in shortly afterwards – depending on the data it receives from the computer. For people, this naturally means that they must be constantly informed about all options and production processes. Communication with machines must be appropriately understandable and user-friendly.
The Achilles’ heel of Industry 4.0 is its data networks. The functioning of the factory of tomorrow depends on terabytes of data being transmitted and processed in the shortest possible time. Even the smallest program error can have fatal consequences – not to mention deliberate manipulation by hackers or saboteurs.
How can we support you to design your next system?

Agile Working Methods
for short product development cycles
Industry 4.0 is still primarily a project for the future, but the first companies are already moving in the direction of smart factories. As a leading production location in Central Europe, Germany has a special interest in turning its vision into reality. But where the journey ultimately leads is still open in many areas.
Flexible Project Management
Agile working methods are also an important method in product development. The basic idea behind this is that many projects are extremely complex and cannot be included in a comprehensive plan beforehand. Instead of creating detailed specification sheets for an overall project, sub-projects are defined with clear objectives. A dense cycle of sprint meetings and collaboration between product owners and project coaches ensure a rapid and customer-oriented development process. Small, interdisciplinary teams work on defined functional patterns, based on which the entire further development is then implemented.
LASER COMPONENTS’ development team was trained in agile development methods at the end of 2018. This method was successfully applied for the first time in the development of the ALBALUX FM white light source. In just a few weeks, the team implemented the customer’s specifications and developed a product that was presented at SPIE Photonics West in February and will also be featured at LASER World of Photonics in June.
LASER COMPONENTS Germany - Your competent partner for optical and optoelectronic components in Germany.
Welcome to LASER COMPONENTS Germany GmbH, your expert for photonics components. Each product in our wide range of detectors, laser diodes, laser modules, optics, fiber optics, and more is worth every Euro (€/EUR). Our customized solutions cover all conceivable areas of application: from sensor technology to medical technology. You can reach us here:
Werner-von-Siemens-Str. 15
82140 Olching
Deutschland
Phone: +49 8142 2864-0
Email: info(at)







