Thin film polarizers are used for polarization separation. They are particularly well suited for high laser powers and UV wavelengths.
Broadband plate polarizers with low dispersions are mainly used in systems that cover a wide wavelength range - for example, in Ti:sapphire fs lasers.
Thin Film Polarizers
Thin-film polarizers are used to separate the polarization states of light waves. These optics are well suited for high laser powers and UV wavelengths.
Our polarizers are manufactured using the IAD or IBS coating process. Both methods allow thin layers, which is very useful for generating complex designs. For example, they enable high-power thin-film polarizers to be used over the entire angular range from 53° to 59°. To ensure a high quality standard, our coating processes are controlled by broadband monitoring.
Working Principle. Thin-film polarizers are installed at the Brewster angle of ≈ 56°. An antireflection coating on the back is not necessary; thus the polarizer can only be used in one direction of the optical axis. A good extinction rate is achieved due to the TFP coating on the front side.
Good to Know
When using and installing the thin-film polarizers it should be taken into account that the p-polarized beam experiences a slight beam offset and the s-polarized beam is deflected by ≈ 112°.
Adjustment-free High Power Thin-film Polarizers
These polarizers are manufactured using an IAD process. In addition, the coating process for these polarizers is supervised using a broadband monitoring technique. The result is a high power thin-film polarizer that can be used at any angle from 53° to 59°. Available wavelengths range from 450 nm to 1064 nm.
One major advancement is the improved specifications for significantly higher transmission and reflection values. More information can be found in our datasheet.
Broadband Plate Polarizers
The coating of broadband plate polarizers is optimized for low dispersion, which makes them particularly suitable for polarization separation of broadband systems such as Ti:sapphire fs-lasers. They are coated on both sides and can therefore be used in both directions.
Working Principle. Plate polarizers are typically manufactured with identical coatings on both sides and installed at an angle of ≈ 72° to the incident beam.
Please note during development and installation that the p-polarized beam will experience a beam offset and the s-polarized beam will be deflected by ≈ 144°.
Specialized Thin-Film Polarizers
Polarizers for angles of incidence (AOI) of 45° can be easily integrated into optical setups. These special optics are typically manufactured with an AR coating on the rear side, since their AOI does not correspond to the Brewster angle.
LASER COMPONENTS also manufactures thin-film polarizers for two or three wavelengths.
Upon request, we also check the possibilities of integrating other optical functions into your thin-film polarizers - for example, additional HR or HT areas or a beam splitter function.
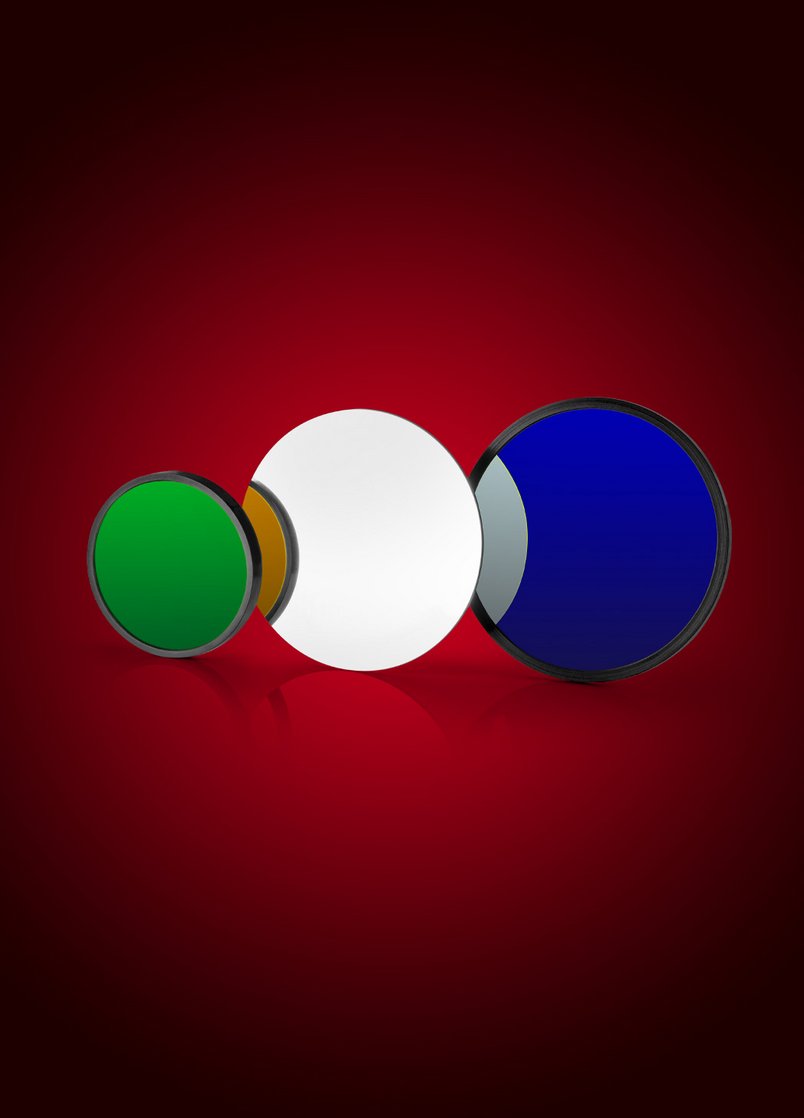
Trichroic Polarization Optics
Using a coating design from LASER COMPONENTS, the trichroic thin film polarizer is able to separate the polarizations of three wavelengths at the same time. At an angle of incidence of 45°, the optic provides very high reflectivity for the s-polarization of the selected wavelengths, while the p-polarization is almost completely transmitted.
The polarizer has been designed for blue (450 nm), green (520 nm) and red light (640 nm), but we can also create designs for other wavelengths upon request.
These types of polarizers can be used to combine linearly polarized laser beams from multiple sources or mix the three wavelengths. It is also possible to combine lasers with the same wavelength and different polarization. The other way around, it is also possible to simultaneously separate unpolarized light at three wavelengths its two polarizations.
Contact
Do you need a quote?
Request your customized laser optics here:

Click here
News & Events
Laser Optics
Accessories
Beyond Borders


Our conversion screens make your laser visible in the range from 250-600 nm, 700-1700 nm, and 1.5 20 µm.